- Most carbon calculators overlook Scope 3 emissions, leading to incomplete data and potential greenwashing.
- Businesses need a holistic approach: data transparency, full lifecycle analysis, and science-based targets.
- Real decarbonization can be achieved through AI-powered platforms that delivers accurate, end-to-end emissions insights.
Enterprises are now regularly facing mounting pressure to measure and reduce their carbon footprint. Regulatory changes, growing environmental awareness, and the lack of comprehensive solutions have intensified the need for companies to take decisive action. This pressure to address climate change has given rise to the widespread adoption of carbon emissions calculators as instrumental tools in the pursuit of a sustainable future. These carbon footprint calculators have emerged as indispensable instruments, enabling businesses to quantify their environmental impact.
This blog explores the challenges of generic carbon emissions calculators and advocates for a more holistic approach to emission mitigation.
Falling Short in Data: Generic Carbon Emissions Calculators
While carbon emissions calculators for businesses are easy to find, their generic nature often leads to significant limitations. These types of carbon emission calculators typically focus on Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions while neglecting Scope 3, which includes indirect emissions from upstream and downstream activities. Obtaining accurate and comprehensive data from such intricate operations presents a significant challenge for businesses. Moreover, oversimplified assumptions and calculations in generic calculators can yield misleading results, leaving businesses with a false sense of their environmental impact. This can lead to accidental greenwashing, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. Additionally, these calculators often lack actionable insights, providing little guidance on effective carbon reduction strategies. Generic emissions calculators, while accessible, ultimately handicap rather than enable companies to achieve their sustainability goals.
A Holistic Approach to Carbon Reduction
To address these limitations, businesses must adopt a more comprehensive and nuanced approach to carbon reduction:
- Invest in data transparency: The foundation of effective carbon reduction lies in robust data collection and analysis systems. Businesses should invest in technologies that provide transparency into all emissions sources across complex supply chains, enabling accurate measurement and targeted reduction efforts.
- Consider a product’s entire lifecycle: Going beyond the traditional focus on direct emissions, businesses should consider the full environmental impact of products and services. This approach, often referred to as Product Carbon Footprinting (PCF), involves assessing the total emissions generated by a product from the cradle to the grave, i.e. from the time natural resources are extracted from the ground and processed through each subsequent stage of manufacturing, transportation, product use, and disposal. Additionally, engaging with suppliers to address Scope 3 emissions is crucial for a holistic carbon reduction strategy.
- Prioritize science-based targets: To make a meaningful impact, enterprises should set ambitious, yet achievable emissions reduction goals aligned with climate science. Science-based targets such as those developed by the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi), provide a useful framework for businesses to develop clear emissions reduction goals aligned with global climate strategy.
- Identify and prioritize decarbonization levers: Enterprises seeking to develop an effective decarbonization strategy must identify specific actions and strategies, referred to as levers, that target the most significant emission hotspots in their value chains. Enterprises can explore initiatives such as adopting renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and engaging in sustainable procurement practices.


Easily Calculate Your Carbon Footprint
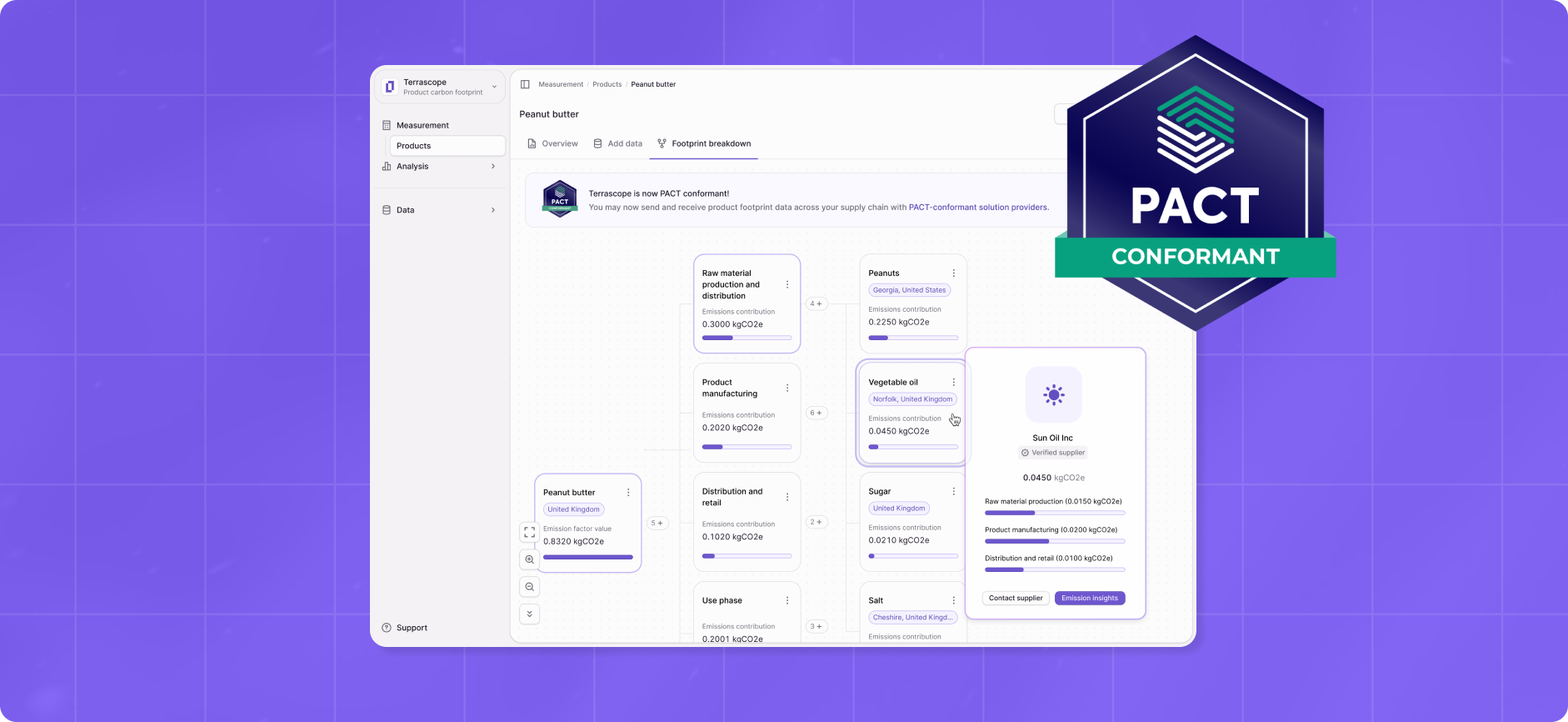
Terrascope’s end-to-end decarbonization platform is designed to help businesses measure, manage, and reduce their emissions. Terrascope harnesses the power of AI and machine learning to easily assimilate data across global supply chains and bridge data gaps as well. Our expertise extends beyond generic carbon footprint calculators and offers tailored data, analytics, and digital tools to help enterprises decarbonize their business operations and supply chains with precision and impact. Unique insights that businesses can gain by working with Terrascope include:
- Identifying emissions hotspots by country, business unit, factory, or process, and pinpointing hotspots with the highest emission contributions for the most impactful decarbonization actions.
- Locating gaps in data quality, comprehensiveness, and granularity, allowing you to gauge the accuracy of existing measurements and decide where to focus data collection efforts for greater material impact.
- Curating a guided visual workflow for suppliers to more seamlessly submit the right data, in the right format, and at the same time gaining insight into how the data will be used.
- Collaborating actively with our Sustainability Experts and Carbon Data Analysts who are ready to provide guidance to your teams.
- Utilizing Terrascope’s unique Activity Lineage feature, which identifies the factors driving year-on-year changes in emissions measurements, uncovering any inconsistencies in approach, data coverage, data granularity or emission factors used.
Our proprietary data confidence methodology provides greater certainty and credibility to your emissions measurement and disclosures. By providing seamless access to data measurement and management, businesses we work with can confidently make informed decisions about their carbon reduction measures.
As the world grapples with the urgent challenges of climate change, the role of enterprises in reducing their carbon footprint cannot be overstated. While generic carbon footprint calculators have been a starting point, they fall short of providing the depth and precision necessary for meaningful carbon reduction. There is a dire need for enterprises to take on a more holistic approach, such as by investing in data transparency, considering the entire product lifecycle, prioritizing science-based targets, and prioritizing decarbonization levers. Terrascope offers tailored solutions to guide enterprises on their journey toward sustainability and help them make strides towards their emission reduction goals.
Reduce your carbon footprint and achieve your sustainability goals with Terrascope’s AI-powered platform.